
IoT sensors can be used for remote borehole monitoring of water levels/depth, water temperature, and parameters such as pH and turbidity. Real-time monitoring coupled with LoRaWAN and cloud technology means data can be transmitted 15KM wirelessly or anywhere in the world using low-power satellite technologies.
Real-time borehole monitoring with IoT
Low-power IoT sensors can monitor a range of parameters relating to boreholes and groundwater sources:
- Water depth/levels
- Water temperature
- pH, Turbidity and ORP
- Salinity/Suspended solids
- Ions and contaminants
- Tamper protection
- Pump status/power consumption
Borehole types
While most people associate boreholes with drinking water (potable), there are many other applications for boreholes:
- Geological surveys
- Monitoring aquifers
- Irrigation
- Groundwater sampling / Groundwater monitoring boreholes
- Drinking water
- Saline intrusion
- Leach agents (from landfills or waste disposal sites)
Borehole Diagram
The diagram below shows the typical cross-section of a borehole. Items such as pumps, pipework and filters have been left out for clarity.
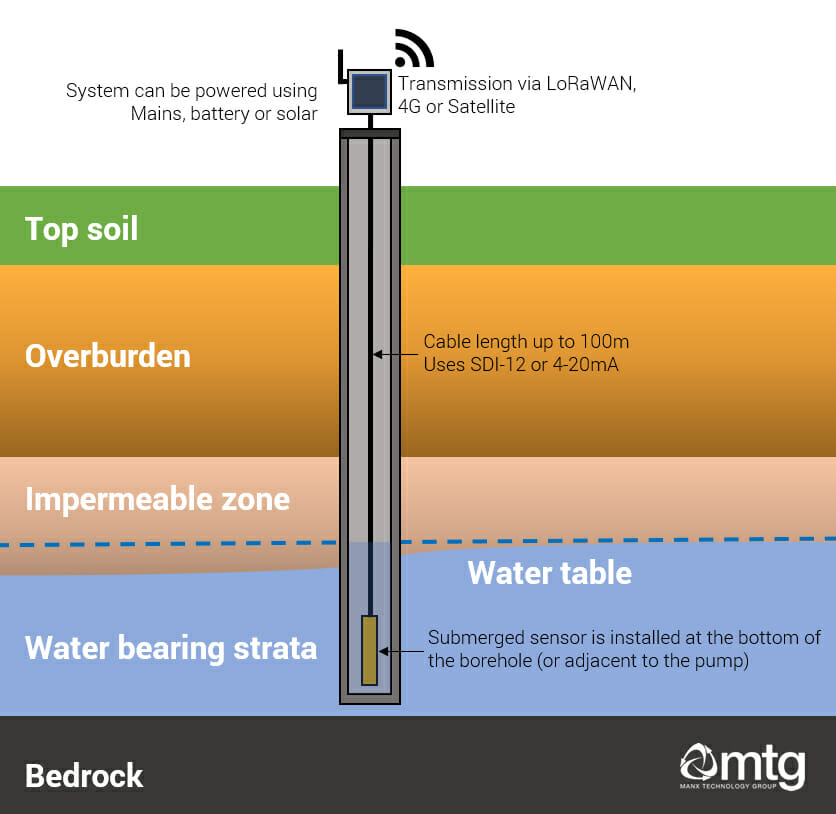
How do I monitor boreholes remotely?
We favour IoT technology to provide real-time monitoring of boreholes. Our solution architecture consists of the following:
IoT Sensor node

The IoT sensor node handles the processing and communication from the IoT sensors. A wide range of communication methods is available, including 4G, LoRaWAN, Satellite, and WiFi.
The flexibility of IoT technology means our systems are suitable for urban, rural or extremely remote operations (without power or mobile networks). The low power operation of the system means it is ideally suited for battery, solar or wind power – capable of operating autonomously for years.
The equipment we use is IP67 rated and suitable for operating in harsh environments.
IoT Sensors
Each node supports various sensors (mentioned previously) – but it is common for a single node to support water levels, temperature and other parameters relevant to the particular use case.
Where there is a need for security or to maintain the integrity of the borehole, additional security sensors can be used to detect tampering.
Visualisation / Dashboards
The node transmits sensor data to the cloud, where it can be visualised and monitored. You can configure thresholds (i.e. water levels, temperature) that, once exceeded, generate alerts and notify critical people of the event.
The real-time nature of the borehole monitoring system means you can identify trends relating to levels, demand, temperature etc.
How often are measurements taken?
The IoT monitoring system can be configured for monitoring intervals of from five minutes to once a day. The measurement interval depends on the borehole application and the power budget (more frequent measurements consume more power).
The user can define the measurement interval when sensor data is transmitted; however, notifications relating to tamper protection or alarms are sent instantly.
Features
- Low power operation. It runs from mains, battery+solar, or long-life battery.
- Up to 100m cable length.
- IP67/IP68 rated, with an impact protection rating of IK09.
- Optional tamper alerts.
- Cloud-ready – with rich visualisation and monitoring.
- Key measurements
- Water levels/depth.
- Temperature.
- Advanced measurements
- Communications
- LoRaWAN – Long-range wireless (up to 15KM).
- WiFi – Local connectivity to broadband.
- 4G – Connection via the cellular network.
- Satellite – Global connectivity for remote deployments.
Where are the sensors installed?
Depth and temperature

The water level and temperature are measured using a sensor lowered into the bottom of the borehole – where it measures the pressure (to determine depth) and temperature. The data is transmitted through the cable to the sensor node.
Water quality (i.e. conductivity, ORP, salinity and pH)
Parameters relating to water quality are monitored in the pipework leading from the borehole using a sampling point or a connection into the pipe.
Find out more
To learn more about our range of Borehole monitoring systems using IoT – please get in touch.
More information
If you would like to learn more about our products and services, request pricing, or discuss a project requirement - you can MTG using the details below. Alternatively, you can e-mail sales@mtg.im for more information.

